Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Tree-LSTM in DGL
Author: Zihao Ye, Qipeng Guo, Minjie Wang, Jake Zhao, Zheng Zhang
Warning
The tutorial aims at gaining insights into the paper, with code as a mean of explanation. The implementation thus is NOT optimized for running efficiency. For recommended implementation, please refer to the official examples.
import os
In this tutorial, you learn to use Tree-LSTM networks for sentiment analysis. The Tree-LSTM is a generalization of long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to tree-structured network topologies.
The Tree-LSTM structure was first introduced by Kai et. al in an ACL 2015 paper: Improved Semantic Representations From Tree-Structured Long Short-Term Memory Networks. The core idea is to introduce syntactic information for language tasks by extending the chain-structured LSTM to a tree-structured LSTM. The dependency tree and constituency tree techniques are leveraged to obtain a ‘’latent tree’’.
The challenge in training Tree-LSTMs is batching — a standard technique in machine learning to accelerate optimization. However, since trees generally have different shapes by nature, parallization is non-trivial. DGL offers an alternative. Pool all the trees into one single graph then induce the message passing over them, guided by the structure of each tree.
The task and the dataset
The steps here use the
Stanford Sentiment Treebank in
dgl.data. The dataset provides a fine-grained, tree-level sentiment
annotation. There are five classes: Very negative, negative, neutral, positive, and
very positive, which indicate the sentiment in the current subtree. Non-leaf
nodes in a constituency tree do not contain words, so use a special
PAD_WORD token to denote them. During training and inference
their embeddings would be masked to all-zero.
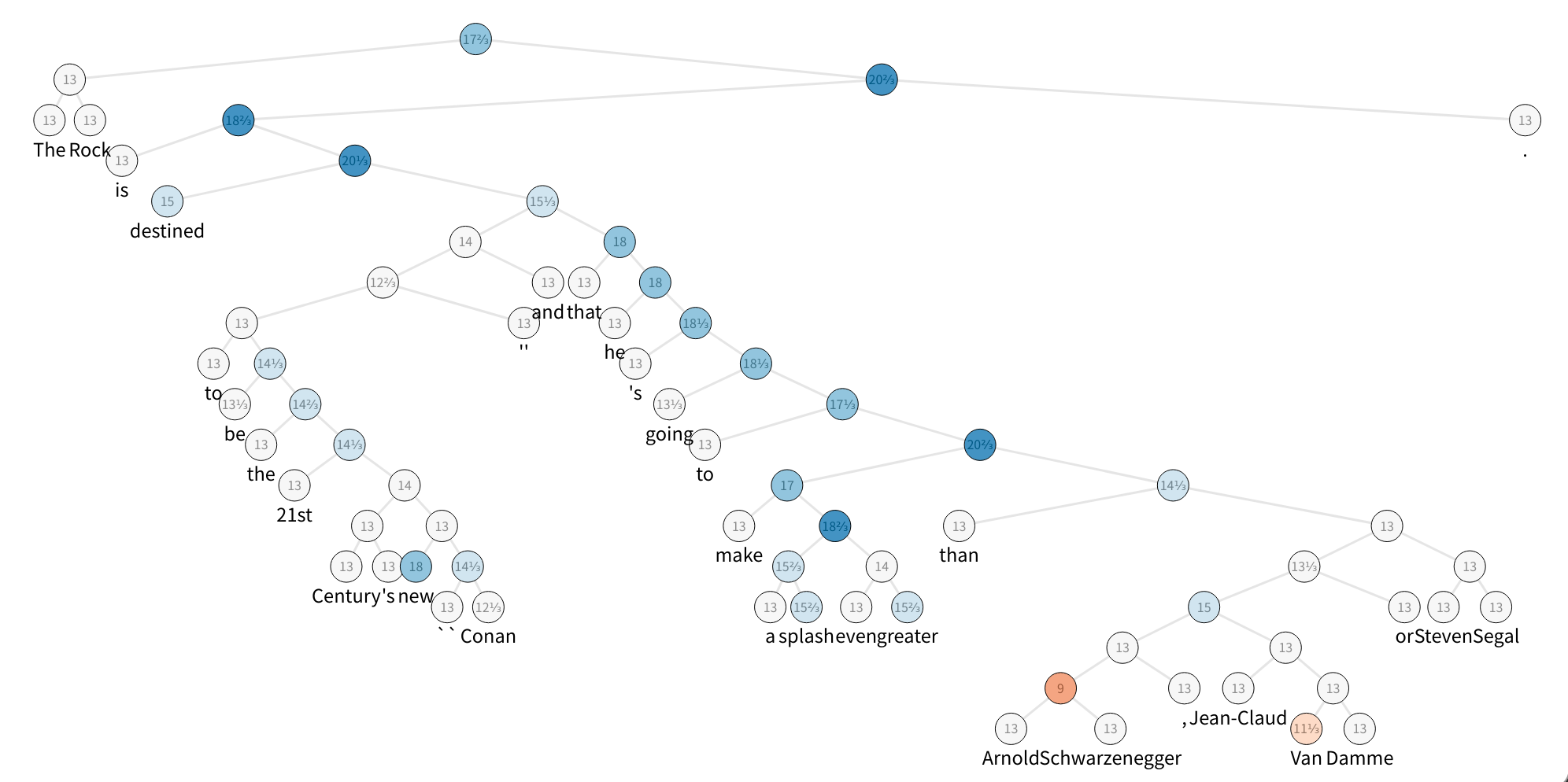
The figure displays one sample of the SST dataset, which is a constituency parse tree with their nodes labeled with sentiment. To speed up things, build a tiny set with five sentences and take a look at the first one.
from collections import namedtuple
os.environ["DGLBACKEND"] = "pytorch"
import dgl
from dgl.data.tree import SSTDataset
SSTBatch = namedtuple("SSTBatch", ["graph", "mask", "wordid", "label"])
# Each sample in the dataset is a constituency tree. The leaf nodes
# represent words. The word is an int value stored in the "x" field.
# The non-leaf nodes have a special word PAD_WORD. The sentiment
# label is stored in the "y" feature field.
trainset = SSTDataset(mode="tiny") # the "tiny" set has only five trees
tiny_sst = [tr for tr in trainset]
num_vocabs = trainset.vocab_size
num_classes = trainset.num_classes
vocab = trainset.vocab # vocabulary dict: key -> id
inv_vocab = {
v: k for k, v in vocab.items()
} # inverted vocabulary dict: id -> word
a_tree = tiny_sst[0]
for token in a_tree.ndata["x"].tolist():
if token != trainset.PAD_WORD:
print(inv_vocab[token], end=" ")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
the rock is destined to be the 21st century 's new `` conan '' and that he 's going to make a splash even greater than arnold schwarzenegger , jean-claud van damme or steven segal .
Step 1: Batching
Add all the trees to one graph, using
the batch() API.
You can read more about the definition of batch(), or
skip ahead to the next step:
.. note:
**Definition**: :func:`~dgl.batch` unions a list of :math:`B`
:class:`~dgl.DGLGraph`\ s and returns a :class:`~dgl.DGLGraph` of batch
size :math:`B`.
- The union includes all the nodes,
edges, and their features. The order of nodes, edges, and features are
preserved.
- Given that you have :math:`V_i` nodes for graph
:math:`\mathcal{G}_i`, the node ID :math:`j` in graph
:math:`\mathcal{G}_i` correspond to node ID
:math:`j + \sum_{k=1}^{i-1} V_k` in the batched graph.
- Therefore, performing feature transformation and message passing on
the batched graph is equivalent to doing those
on all ``DGLGraph`` constituents in parallel.
- Duplicate references to the same graph are
treated as deep copies; the nodes, edges, and features are duplicated,
and mutation on one reference does not affect the other.
- The batched graph keeps track of the meta
information of the constituents so it can be
:func:`~dgl.batched_graph.unbatch`\ ed to list of ``DGLGraph``\ s.
Step 2: Tree-LSTM cell with message-passing APIs
Researchers have proposed two types of Tree-LSTMs: Child-Sum Tree-LSTMs, and \(N\)-ary Tree-LSTMs. In this tutorial you focus on applying Binary Tree-LSTM to binarized constituency trees. This application is also known as Constituency Tree-LSTM. Use PyTorch as a backend framework to set up the network.
In N-ary Tree-LSTM, each unit at node \(j\) maintains a hidden representation \(h_j\) and a memory cell \(c_j\). The unit \(j\) takes the input vector \(x_j\) and the hidden representations of the child units: \(h_{jl}, 1\leq l\leq N\) as input, then update its new hidden representation \(h_j\) and memory cell \(c_j\) by:
It can be decomposed into three phases: message_func,
reduce_func and apply_node_func.
Note
apply_node_func is a new node UDF that has not been introduced before. In
apply_node_func, a user specifies what to do with node features,
without considering edge features and messages. In a Tree-LSTM case,
apply_node_func is a must, since there exists (leaf) nodes with
\(0\) incoming edges, which would not be updated with
reduce_func.
import torch as th
import torch.nn as nn
class TreeLSTMCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, x_size, h_size):
super(TreeLSTMCell, self).__init__()
self.W_iou = nn.Linear(x_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.U_iou = nn.Linear(2 * h_size, 3 * h_size, bias=False)
self.b_iou = nn.Parameter(th.zeros(1, 3 * h_size))
self.U_f = nn.Linear(2 * h_size, 2 * h_size)
def message_func(self, edges):
return {"h": edges.src["h"], "c": edges.src["c"]}
def reduce_func(self, nodes):
# concatenate h_jl for equation (1), (2), (3), (4)
h_cat = nodes.mailbox["h"].view(nodes.mailbox["h"].size(0), -1)
# equation (2)
f = th.sigmoid(self.U_f(h_cat)).view(*nodes.mailbox["h"].size())
# second term of equation (5)
c = th.sum(f * nodes.mailbox["c"], 1)
return {"iou": self.U_iou(h_cat), "c": c}
def apply_node_func(self, nodes):
# equation (1), (3), (4)
iou = nodes.data["iou"] + self.b_iou
i, o, u = th.chunk(iou, 3, 1)
i, o, u = th.sigmoid(i), th.sigmoid(o), th.tanh(u)
# equation (5)
c = i * u + nodes.data["c"]
# equation (6)
h = o * th.tanh(c)
return {"h": h, "c": c}
Step 3: Define traversal
After you define the message-passing functions, induce the right order to trigger them. This is a significant departure from models such as GCN, where all nodes are pulling messages from upstream ones simultaneously.
In the case of Tree-LSTM, messages start from leaves of the tree, and propagate/processed upwards until they reach the roots. A visualization is as follows:
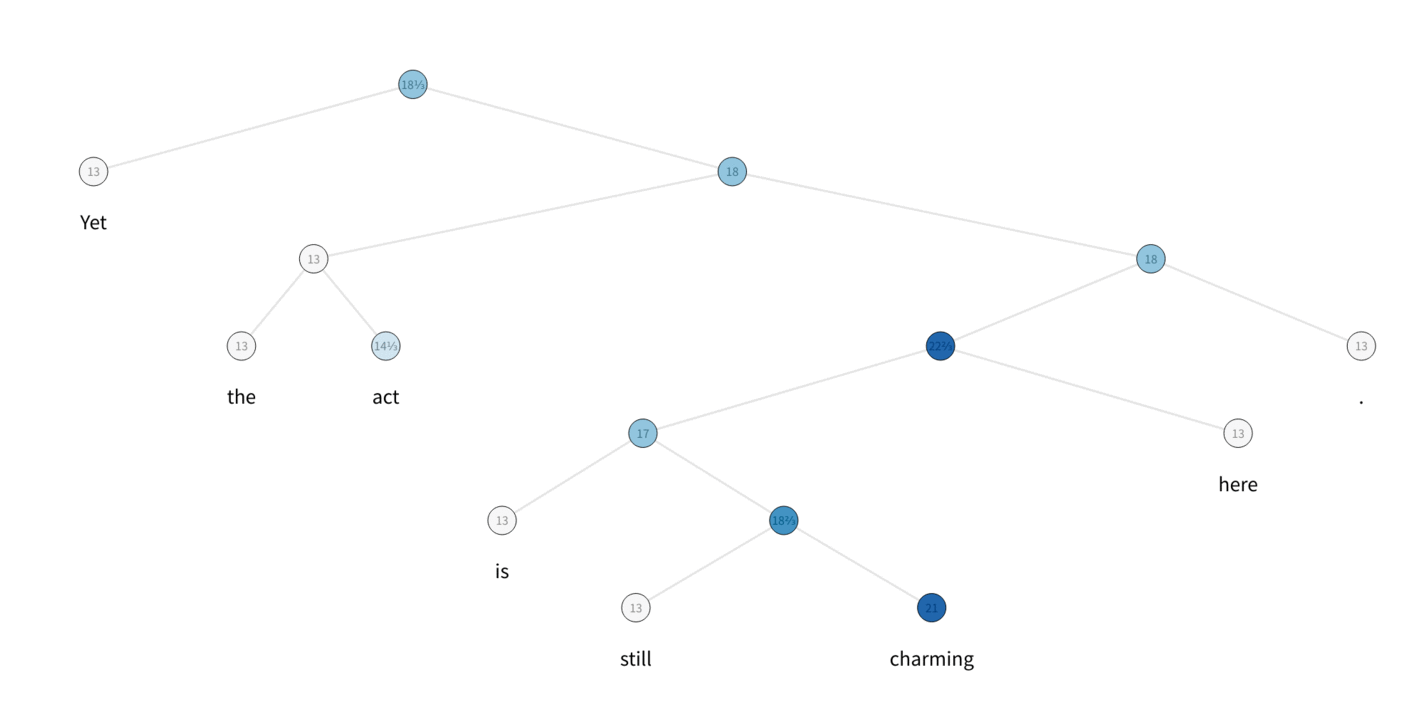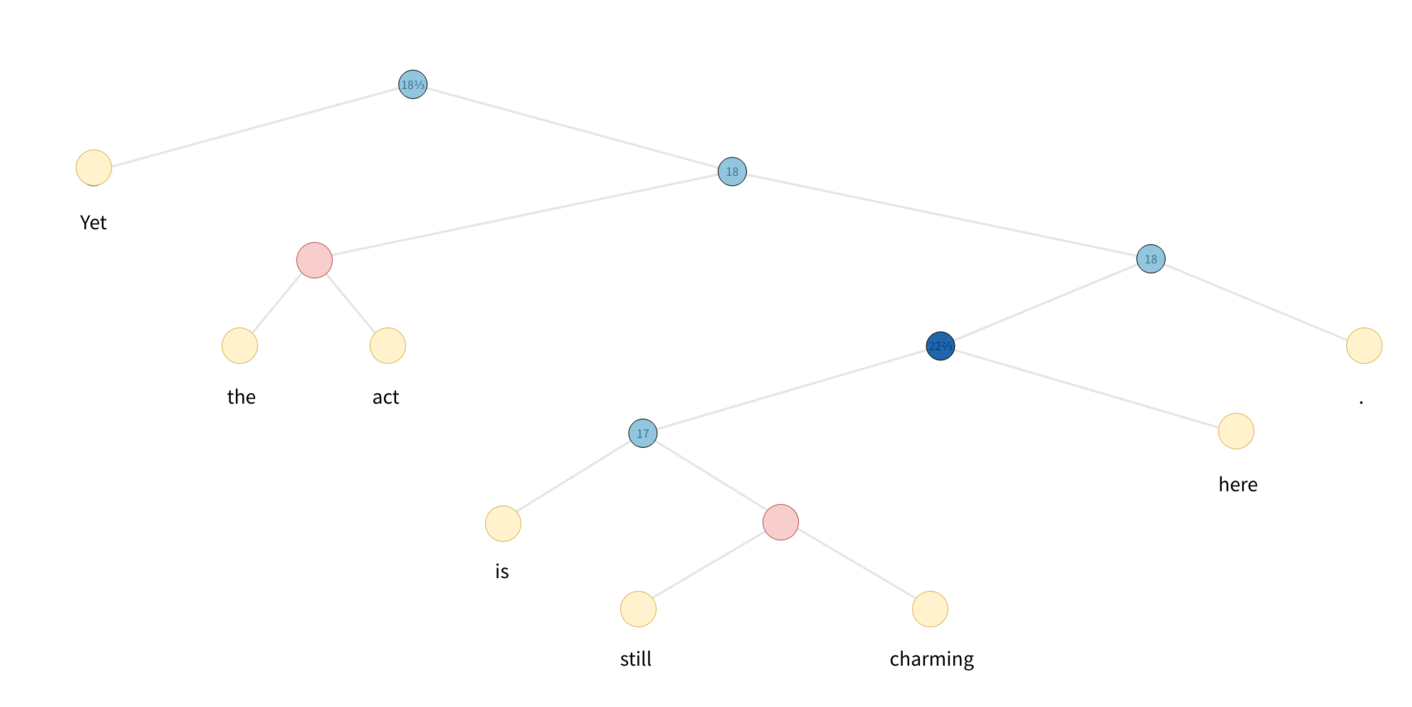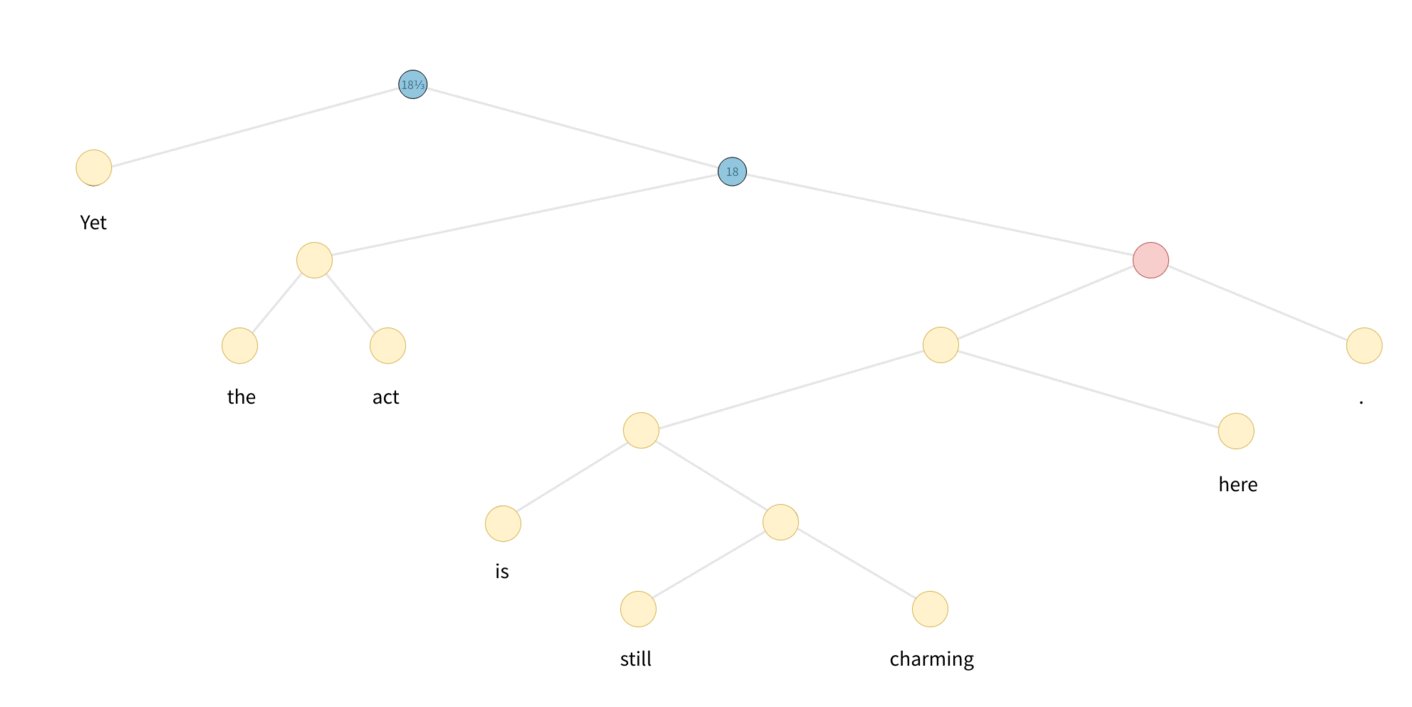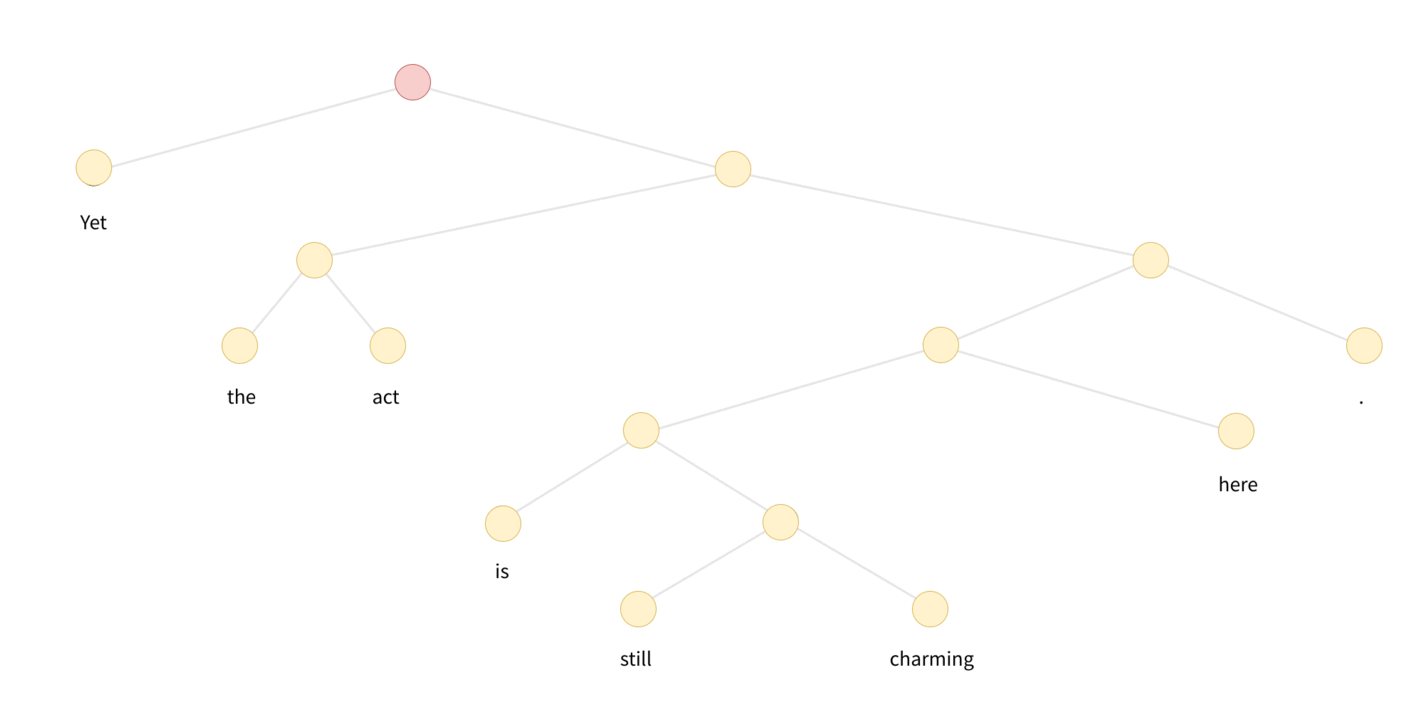
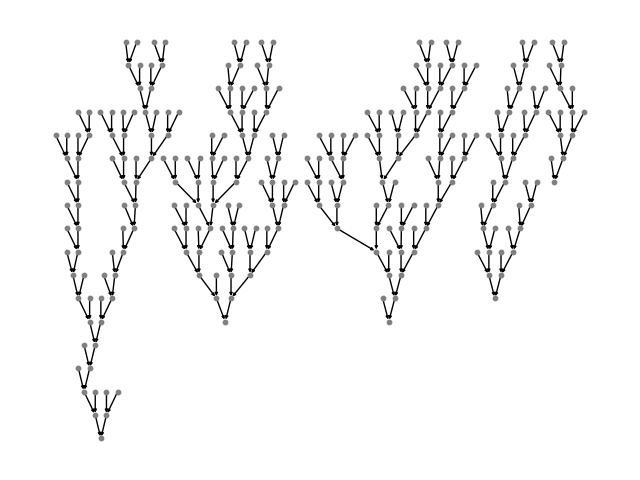
DGL defines a generator to perform the topological sort, each item is a tensor recording the nodes from bottom level to the roots. One can appreciate the degree of parallelism by inspecting the difference of the followings:
# to heterogenous graph
trv_a_tree = dgl.graph(a_tree.edges())
print("Traversing one tree:")
print(dgl.topological_nodes_generator(trv_a_tree))
# to heterogenous graph
trv_graph = dgl.graph(graph.edges())
print("Traversing many trees at the same time:")
print(dgl.topological_nodes_generator(trv_graph))
Traversing one tree:
(tensor([ 2, 3, 6, 8, 13, 15, 17, 19, 22, 23, 25, 27, 28, 29, 30, 32, 34, 36,
38, 40, 43, 46, 47, 49, 50, 52, 58, 59, 60, 62, 64, 65, 66, 68, 69, 70]), tensor([ 1, 21, 26, 45, 48, 57, 63, 67]), tensor([24, 44, 56, 61]), tensor([20, 42, 55]), tensor([18, 54]), tensor([16, 53]), tensor([14, 51]), tensor([12, 41]), tensor([11, 39]), tensor([10, 37]), tensor([35]), tensor([33]), tensor([31]), tensor([9]), tensor([7]), tensor([5]), tensor([4]), tensor([0]))
Traversing many trees at the same time:
(tensor([ 2, 3, 6, 8, 13, 15, 17, 19, 22, 23, 25, 27, 28, 29,
30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 43, 46, 47, 49, 50, 52, 58, 59,
60, 62, 64, 65, 66, 68, 69, 70, 74, 76, 78, 79, 82, 83,
85, 88, 90, 92, 93, 95, 96, 100, 102, 103, 105, 109, 110, 112,
113, 117, 118, 119, 121, 125, 127, 129, 130, 132, 133, 135, 138, 140,
141, 142, 143, 150, 152, 153, 155, 158, 159, 161, 162, 164, 168, 170,
171, 174, 175, 178, 179, 182, 184, 185, 187, 189, 190, 191, 192, 195,
197, 198, 200, 202, 205, 208, 210, 212, 213, 214, 216, 218, 219, 220,
223, 225, 227, 229, 230, 232, 235, 237, 240, 242, 244, 246, 248, 249,
251, 253, 255, 256, 257, 259, 262, 263, 267, 269, 270, 271, 272]), tensor([ 1, 21, 26, 45, 48, 57, 63, 67, 77, 81, 91, 94, 101, 108,
111, 116, 128, 131, 139, 151, 157, 160, 169, 173, 177, 183, 188, 196,
211, 217, 228, 247, 254, 261, 268]), tensor([ 24, 44, 56, 61, 75, 89, 99, 107, 115, 126, 137, 149, 156, 167,
181, 186, 194, 209, 215, 226, 245, 252, 266]), tensor([ 20, 42, 55, 73, 87, 124, 136, 154, 180, 207, 224, 243, 250, 265]), tensor([ 18, 54, 86, 123, 134, 148, 176, 206, 222, 241, 264]), tensor([ 16, 53, 84, 122, 172, 204, 239, 260]), tensor([ 14, 51, 80, 120, 166, 203, 238, 258]), tensor([ 12, 41, 72, 114, 165, 201, 236]), tensor([ 11, 39, 106, 163, 199, 234]), tensor([ 10, 37, 104, 147, 193, 233]), tensor([ 35, 98, 146, 231]), tensor([ 33, 97, 145, 221]), tensor([ 31, 71, 144]), tensor([9]), tensor([7]), tensor([5]), tensor([4]), tensor([0]))
Call prop_nodes() to trigger the message passing:
import dgl.function as fn
import torch as th
trv_graph.ndata["a"] = th.ones(graph.num_nodes(), 1)
traversal_order = dgl.topological_nodes_generator(trv_graph)
trv_graph.prop_nodes(
traversal_order,
message_func=fn.copy_u("a", "a"),
reduce_func=fn.sum("a", "a"),
)
# the following is a syntax sugar that does the same
# dgl.prop_nodes_topo(graph)
Note
Before you call prop_nodes(), specify a
message_func and reduce_func in advance. In the example, you can see built-in
copy-from-source and sum functions as message functions, and a reduce
function for demonstration.
Putting it together
Here is the complete code that specifies the Tree-LSTM class.
class TreeLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
num_vocabs,
x_size,
h_size,
num_classes,
dropout,
pretrained_emb=None,
):
super(TreeLSTM, self).__init__()
self.x_size = x_size
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_vocabs, x_size)
if pretrained_emb is not None:
print("Using glove")
self.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_emb)
self.embedding.weight.requires_grad = True
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.linear = nn.Linear(h_size, num_classes)
self.cell = TreeLSTMCell(x_size, h_size)
def forward(self, batch, h, c):
"""Compute tree-lstm prediction given a batch.
Parameters
----------
batch : dgl.data.SSTBatch
The data batch.
h : Tensor
Initial hidden state.
c : Tensor
Initial cell state.
Returns
-------
logits : Tensor
The prediction of each node.
"""
g = batch.graph
# to heterogenous graph
g = dgl.graph(g.edges())
# feed embedding
embeds = self.embedding(batch.wordid * batch.mask)
g.ndata["iou"] = self.cell.W_iou(
self.dropout(embeds)
) * batch.mask.float().unsqueeze(-1)
g.ndata["h"] = h
g.ndata["c"] = c
# propagate
dgl.prop_nodes_topo(
g,
message_func=self.cell.message_func,
reduce_func=self.cell.reduce_func,
apply_node_func=self.cell.apply_node_func,
)
# compute logits
h = self.dropout(g.ndata.pop("h"))
logits = self.linear(h)
return logits
import torch.nn.functional as F
Main Loop
Finally, you could write a training paradigm in PyTorch.
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
device = th.device("cpu")
# hyper parameters
x_size = 256
h_size = 256
dropout = 0.5
lr = 0.05
weight_decay = 1e-4
epochs = 10
# create the model
model = TreeLSTM(
trainset.vocab_size, x_size, h_size, trainset.num_classes, dropout
)
print(model)
# create the optimizer
optimizer = th.optim.Adagrad(
model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay
)
def batcher(dev):
def batcher_dev(batch):
batch_trees = dgl.batch(batch)
return SSTBatch(
graph=batch_trees,
mask=batch_trees.ndata["mask"].to(device),
wordid=batch_trees.ndata["x"].to(device),
label=batch_trees.ndata["y"].to(device),
)
return batcher_dev
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=tiny_sst,
batch_size=5,
collate_fn=batcher(device),
shuffle=False,
num_workers=0,
)
# training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
for step, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
g = batch.graph
n = g.num_nodes()
h = th.zeros((n, h_size))
c = th.zeros((n, h_size))
logits = model(batch, h, c)
logp = F.log_softmax(logits, 1)
loss = F.nll_loss(logp, batch.label, reduction="sum")
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
pred = th.argmax(logits, 1)
acc = float(th.sum(th.eq(batch.label, pred))) / len(batch.label)
print(
"Epoch {:05d} | Step {:05d} | Loss {:.4f} | Acc {:.4f} |".format(
epoch, step, loss.item(), acc
)
)
TreeLSTM(
(embedding): Embedding(19536, 256)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(linear): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=5, bias=True)
(cell): TreeLSTMCell(
(W_iou): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=768, bias=False)
(U_iou): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=768, bias=False)
(U_f): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
)
)
/home/ubuntu/prod-doc/readthedocs.org/user_builds/dgl/checkouts/latest/python/dgl/core.py:82: DGLWarning: The input graph for the user-defined edge function does not contain valid edges
dgl_warning(
Epoch 00000 | Step 00000 | Loss 439.9816 | Acc 0.2015 |
Epoch 00001 | Step 00000 | Loss 226.3700 | Acc 0.7179 |
Epoch 00002 | Step 00000 | Loss 542.1960 | Acc 0.6190 |
Epoch 00003 | Step 00000 | Loss 474.2100 | Acc 0.7766 |
Epoch 00004 | Step 00000 | Loss 326.0594 | Acc 0.6264 |
Epoch 00005 | Step 00000 | Loss 176.7779 | Acc 0.8352 |
Epoch 00006 | Step 00000 | Loss 116.4029 | Acc 0.8571 |
Epoch 00007 | Step 00000 | Loss 114.9060 | Acc 0.8828 |
Epoch 00008 | Step 00000 | Loss 74.3830 | Acc 0.9267 |
Epoch 00009 | Step 00000 | Loss 65.8115 | Acc 0.9231 |
To train the model on a full dataset with different settings (such as CPU or GPU), refer to the PyTorch example. There is also an implementation of the Child-Sum Tree-LSTM.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.759 seconds)